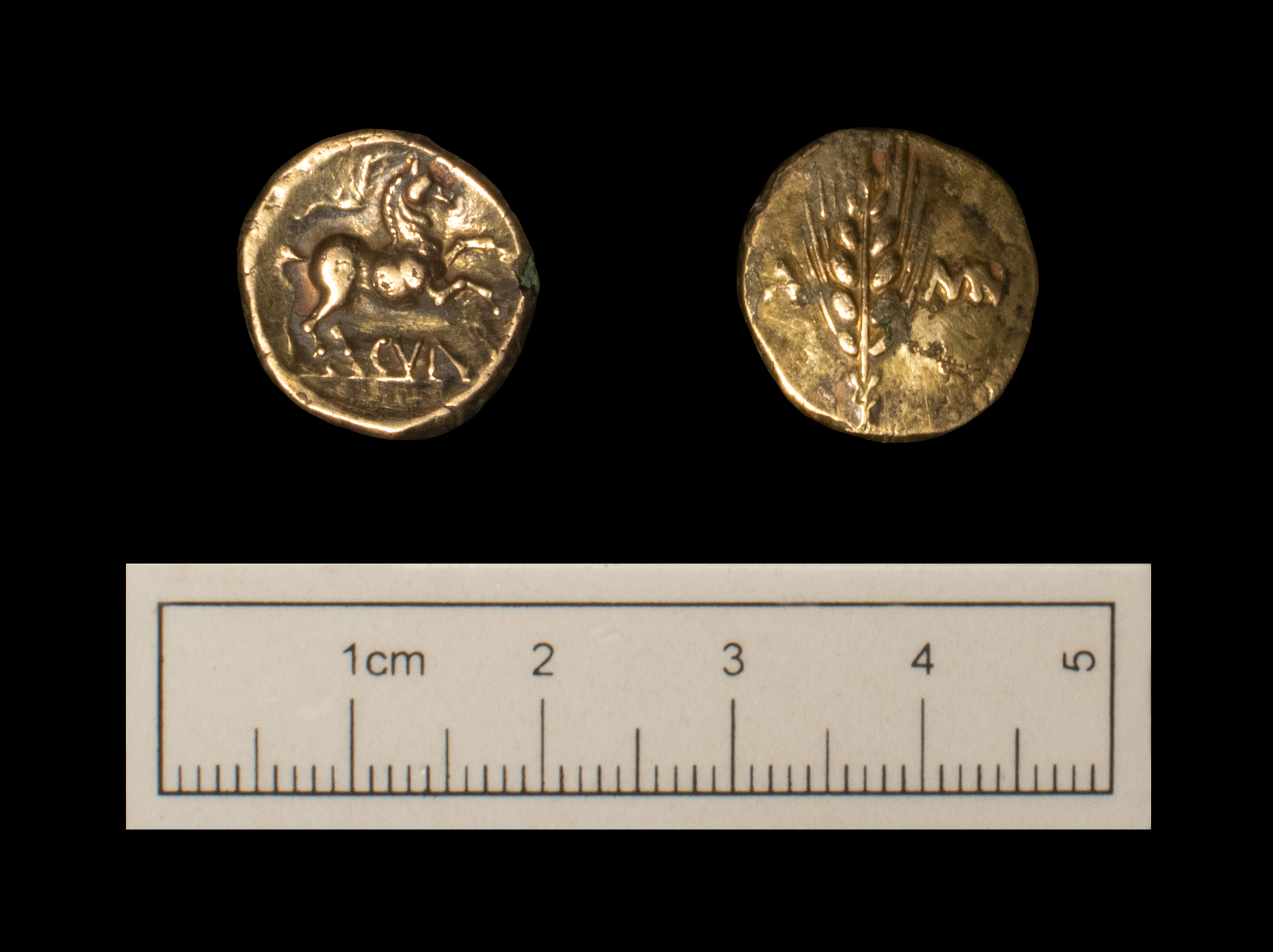
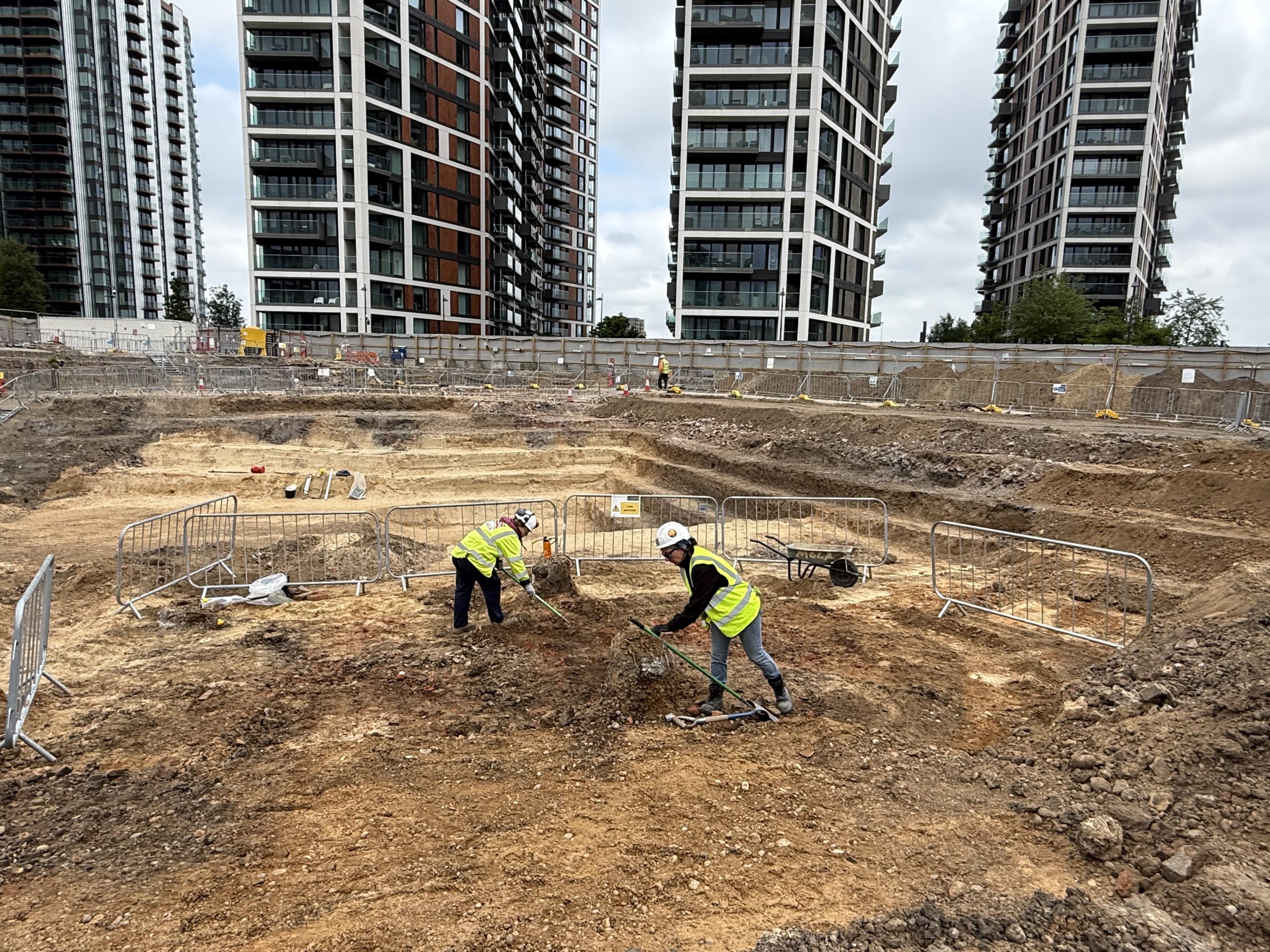
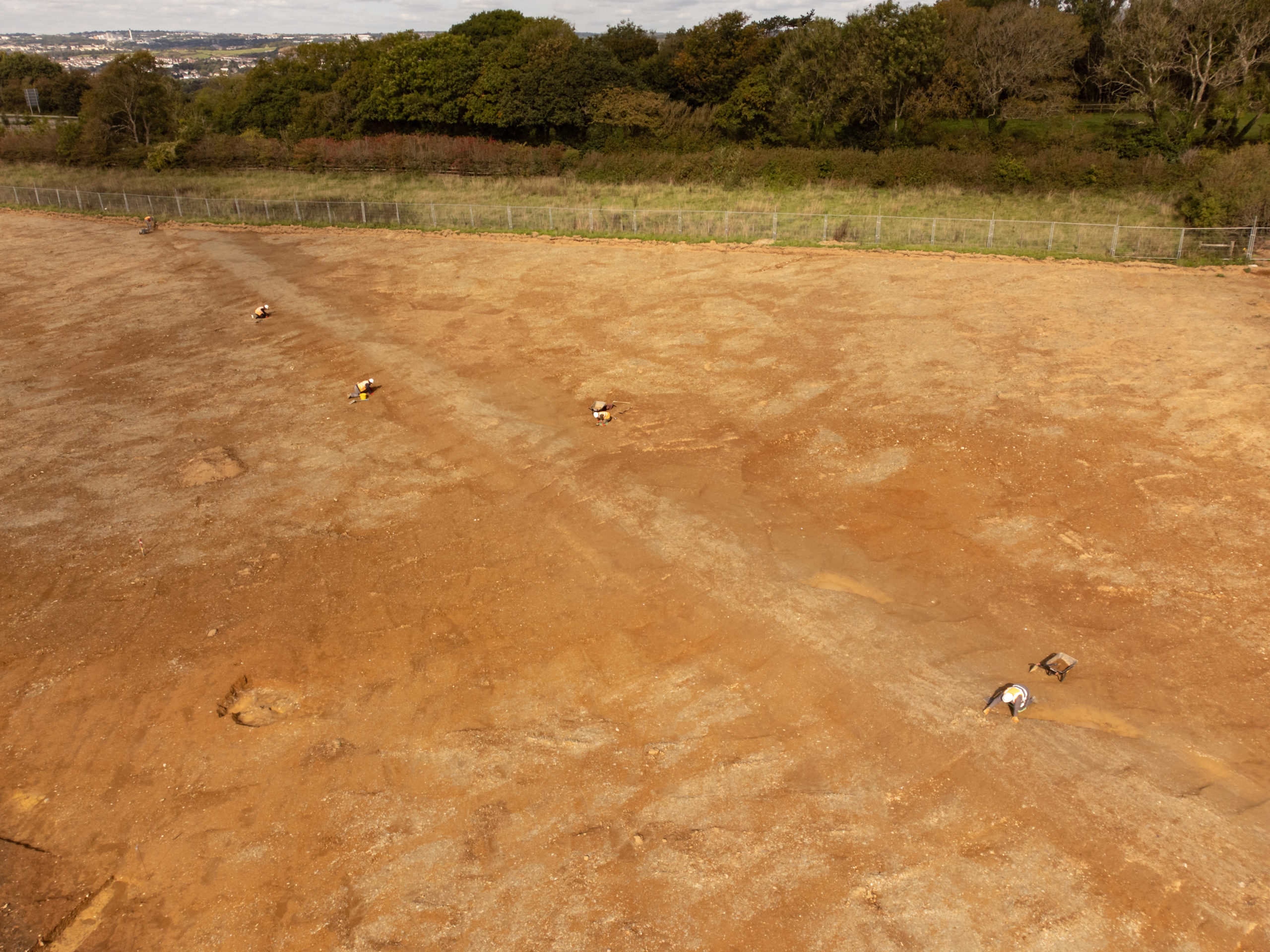
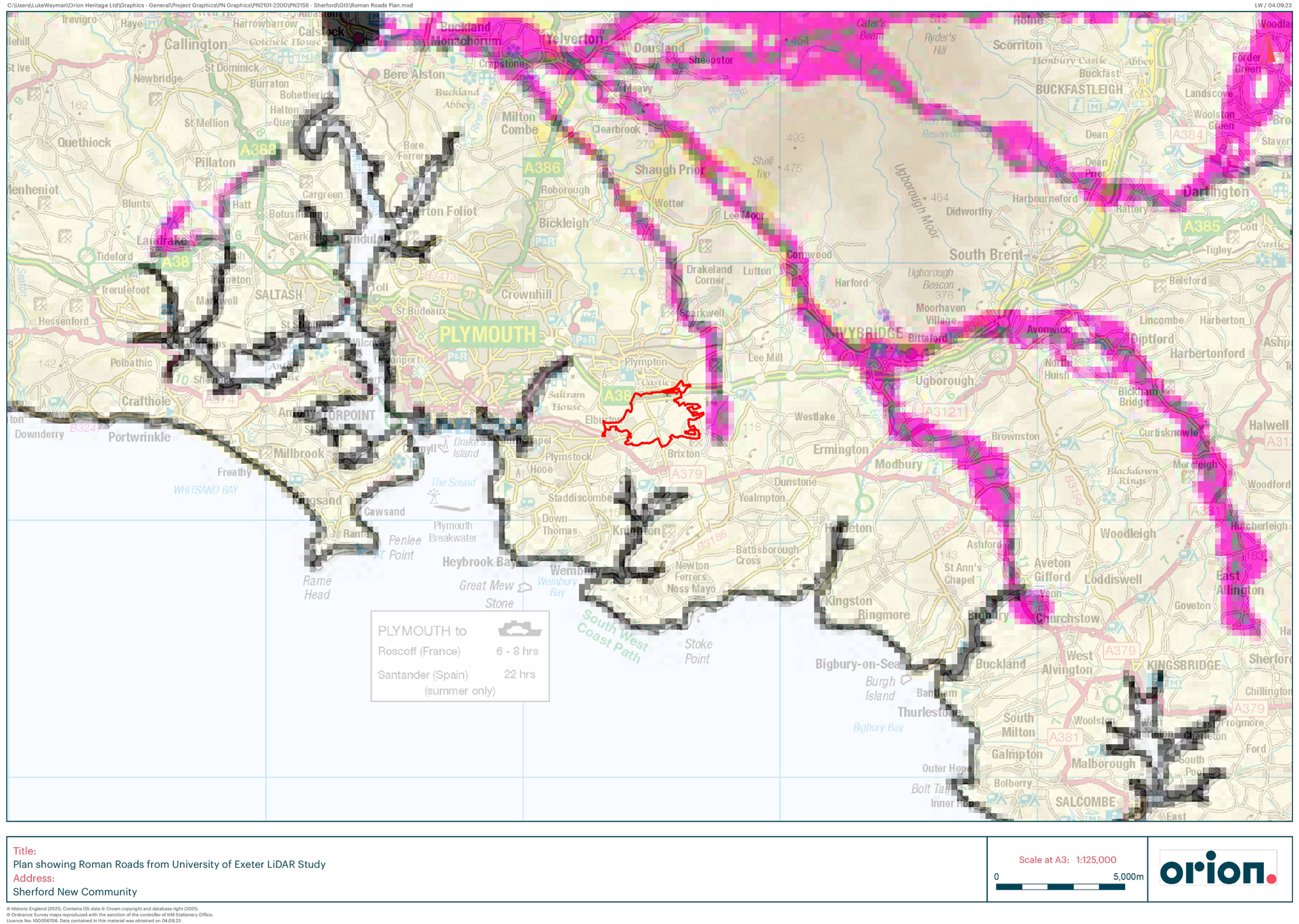
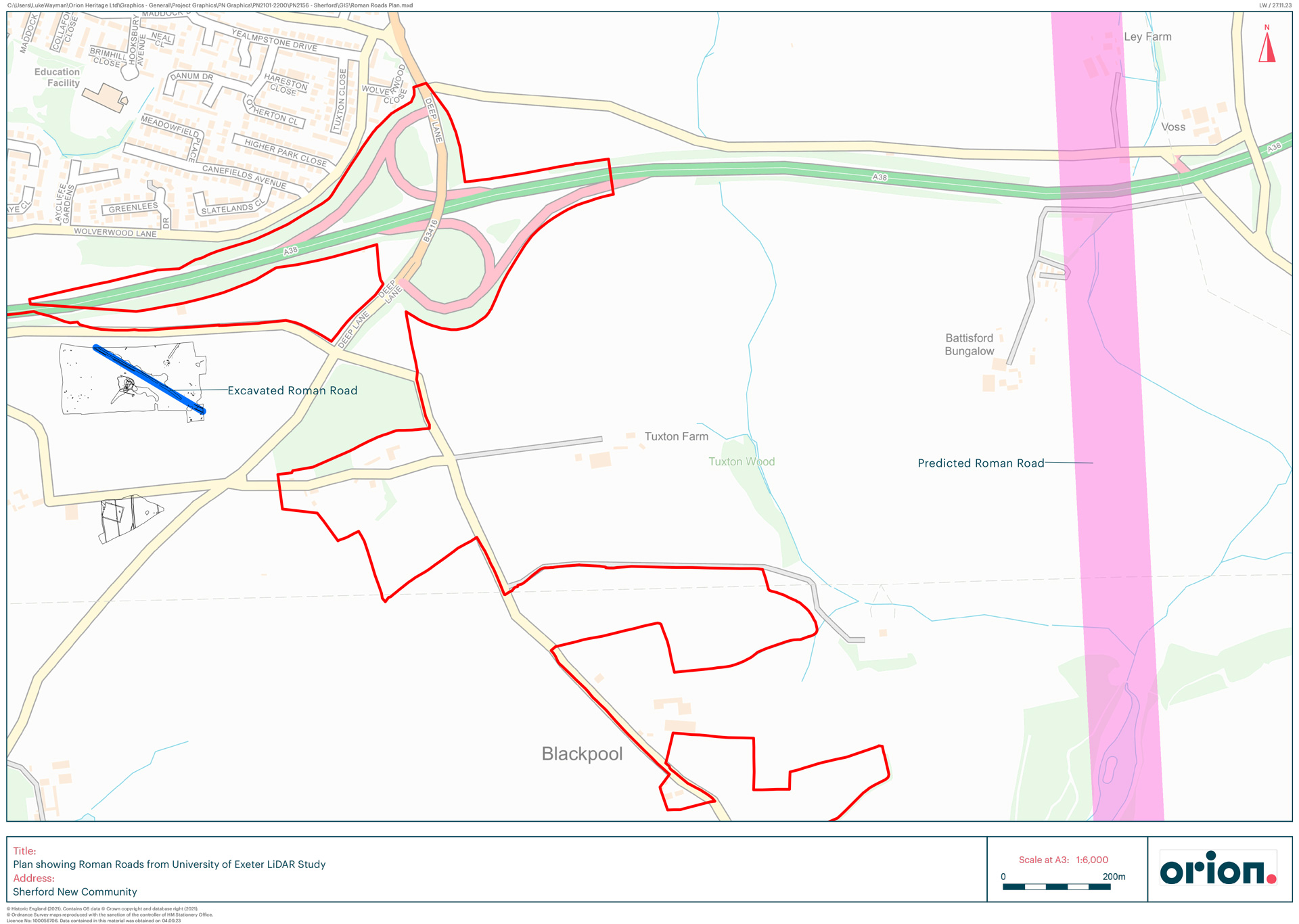
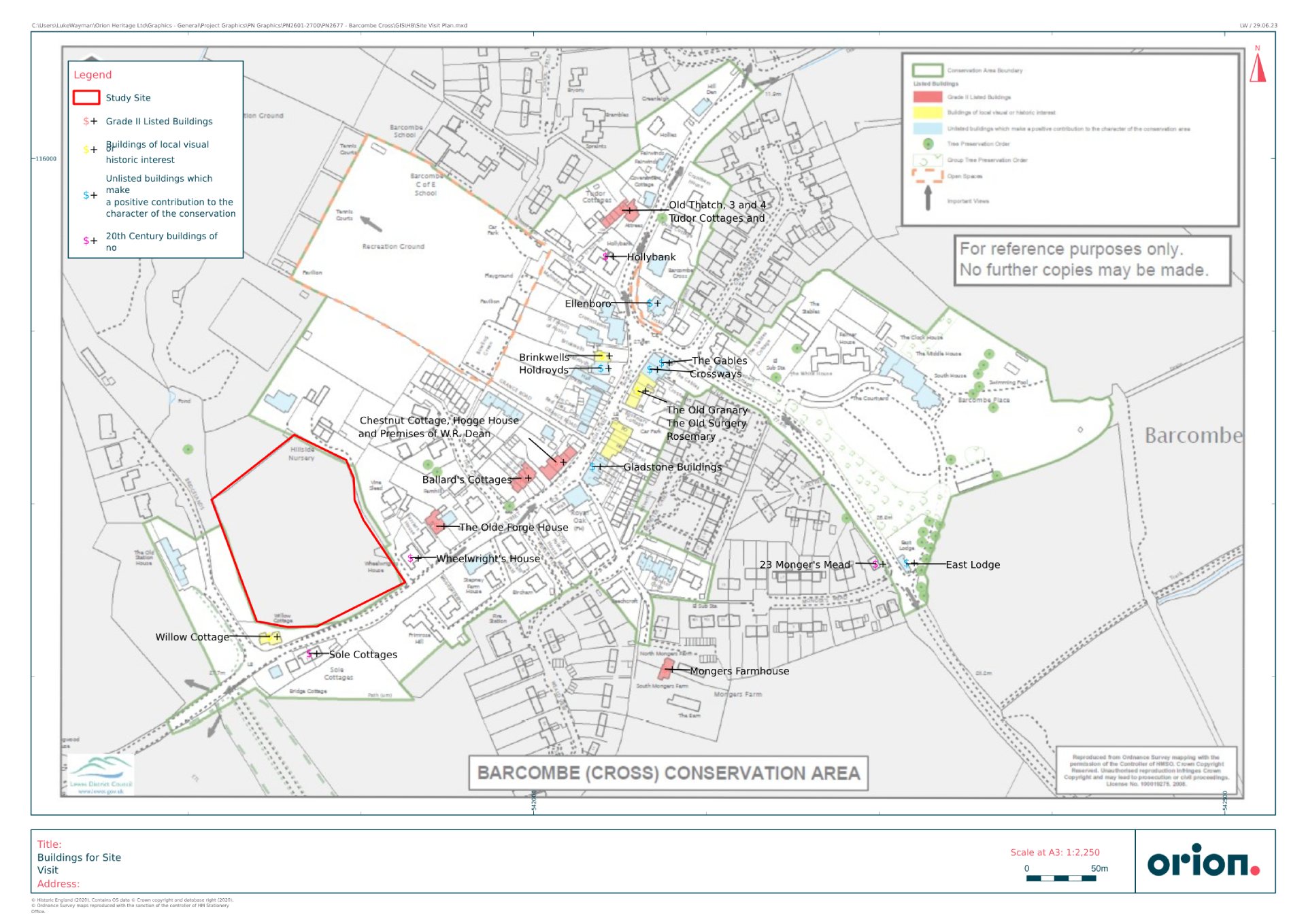
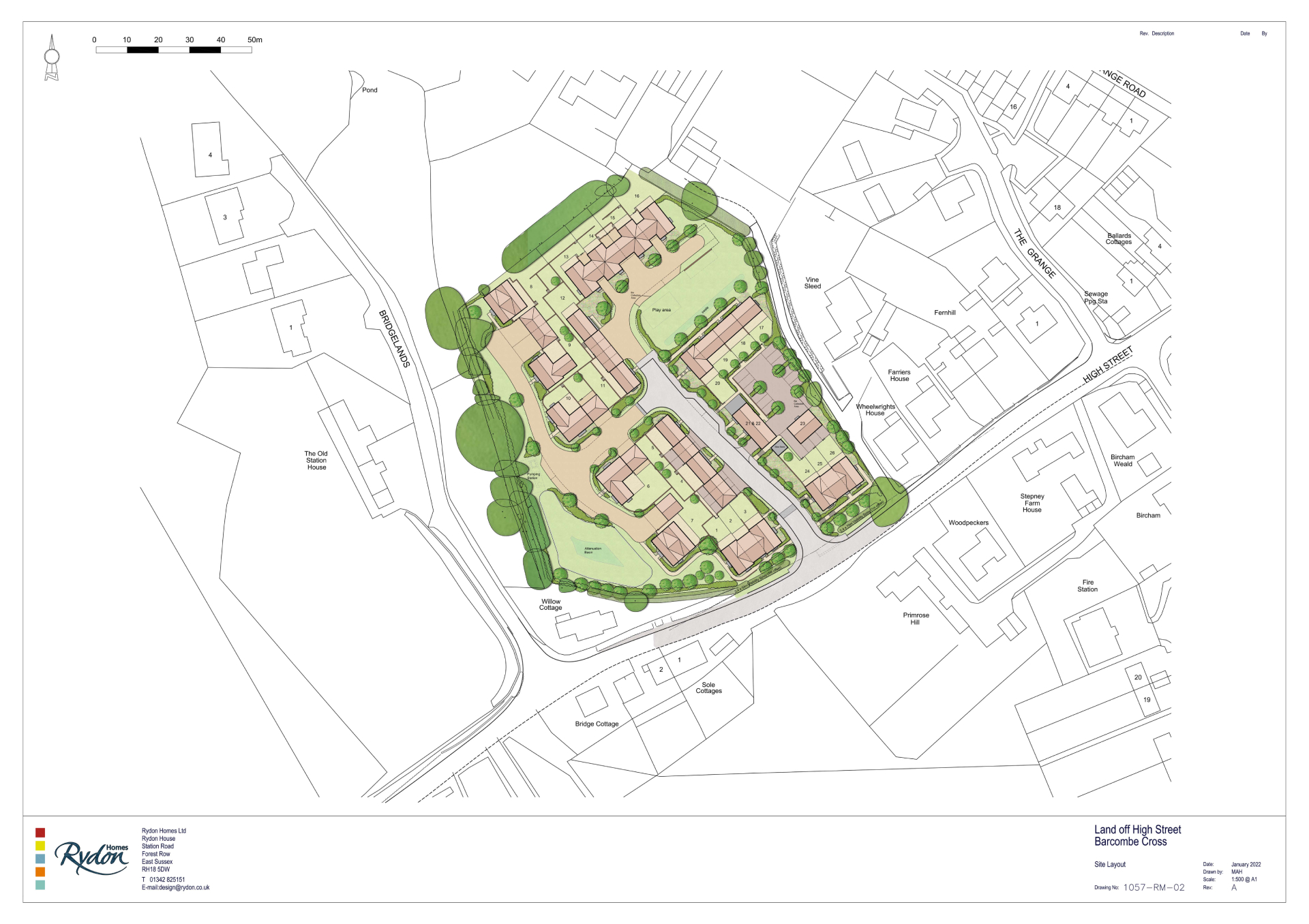
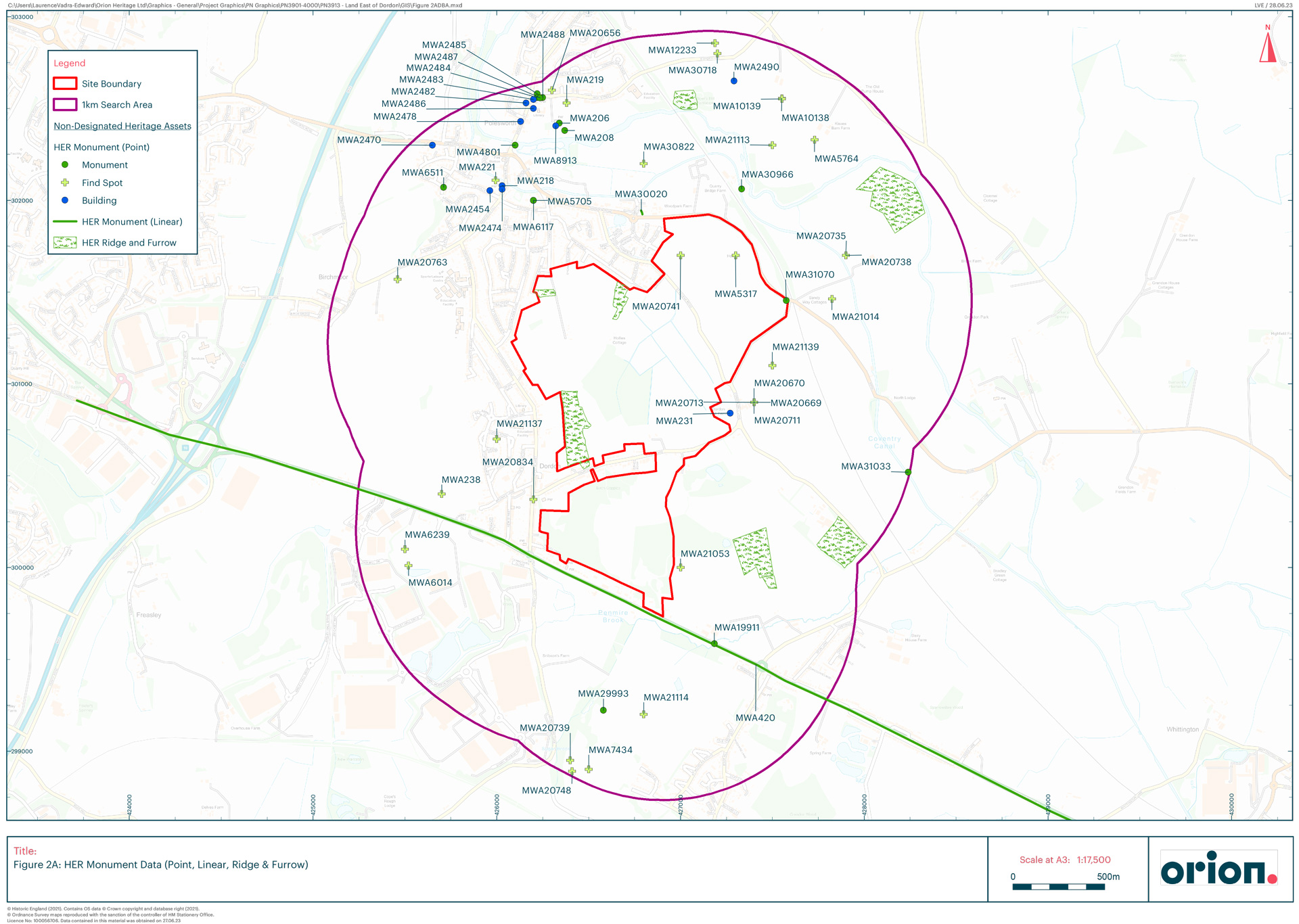
Archaeological remains can survive anywhere and everywhere, often unseen and unsuspected. From fields and villages to towns and cities, archaeology is all around us and shapes our surroundings.
It poses both risks and opportunities for all developments, whether in urban or greenfield locations. There are approximately 34,000 Scheduled monuments in the UK but despite this being a big number, most archaeology that housing schemes affect are non-designated heritage assets. While, as non-designated heritage assets, archaeology is not usually an absolute design constraint, it can present serious design, planning and implementation issues to any development scheme. Due to their land take, this is a risk for major residential schemes.
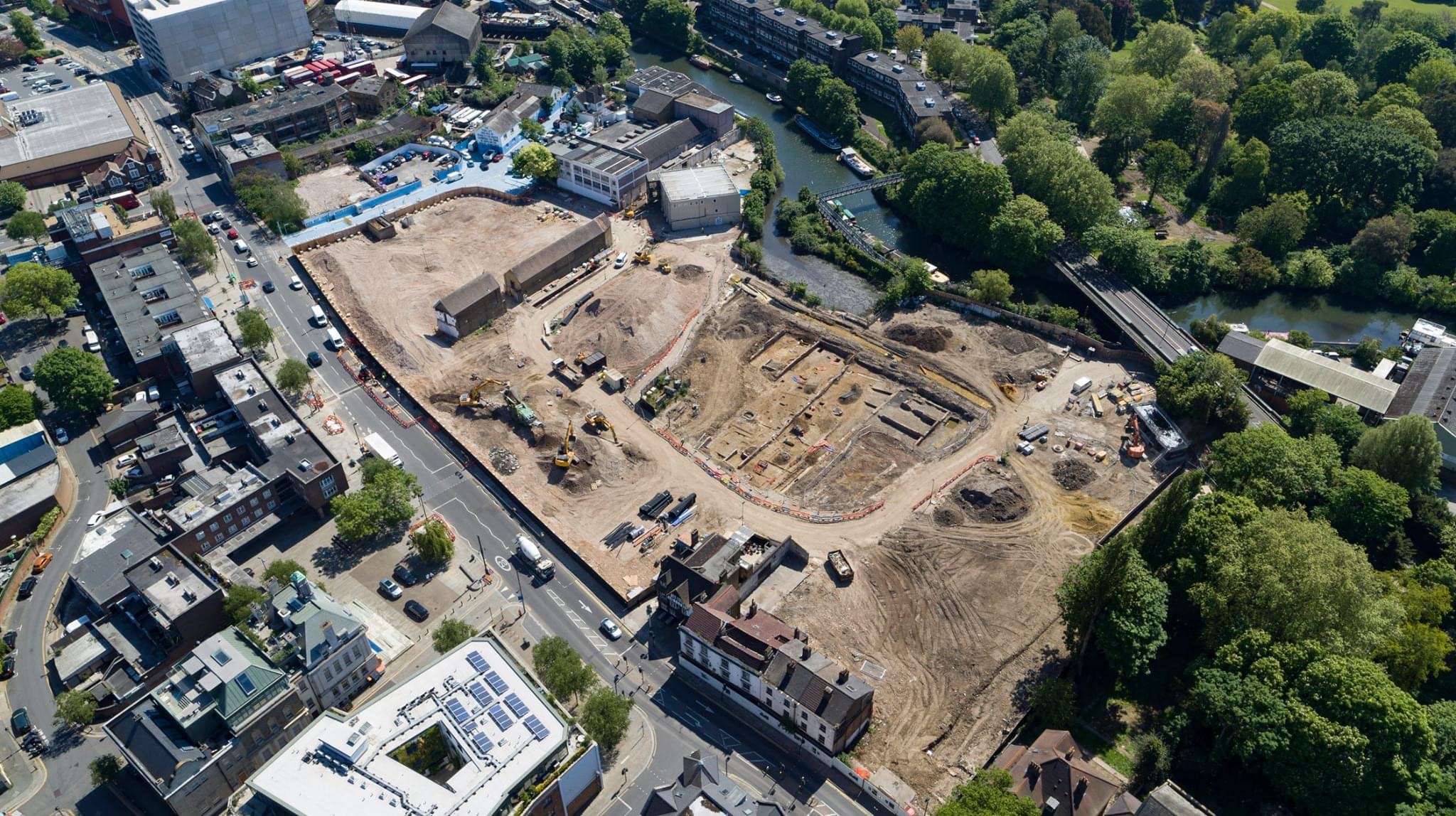

Early Project Planning
If tackled early enough in project planning, most of the challenges archaeology poses, apart from the cost, can be overcome fairly easily. It is when archaeology has not been considered early enough in the development process that things can go wrong with unexpected costs and delays in critical areas. The earlier the archaeological risks can be considered and evaluated, the less likely that archaeological remains become a challenge to development.
Questions to be asked
The earlier the better is the mantra when considering archaeological and heritage matters in the development process. Questions need asking such as – is there anything known archaeology here already? What is known in the wider area and does that have any implications for our site? Is the geology and topography a factor influencing the potential for archaeology? Is there evidence for subtle earthworks not even visible to the eye and what about cropmark evidence? Other questions are also at play, such as, what is the usual approach of the LPA’s archaeological advisors in relation to geophysical survey, trenching sample sizes and predetermination v conditional trenching?
These questions can start to be answered through initial high level appraisal which informs the development’s risks register, its constraints and opportunities assessment and early masterplanning & cost planning.
Assessment & Evaluation
As a proposed residential scheme starts to progress through the Local Plan, outline application and RMA process, the initial high-level assessment gets refined, tested and developed through detailed research, non-intrusive and intrusive archaeological investigation. Such work typically involves desk-based assessment, heritage statement, geophysical survey and/or trenching.

The thorny issue of evaluation trenching, its sample size and whether it is pre-determination or conditional, is almost inevitably going to raise its head at some stage. Although the NPPF does have provision for evaluation trenching, it does not provide guidance on when in the planning process this should happen. Many LPA archaeology advisors now routinely require pre-determination on all green field development sites, but others take a more flexible and (dare we say it) pragmatic approach. There are, of course, many sites where archaeology has been established to be a very serious issue that it is in the developer’s/land promoter’s interest to undertake trenching pre-determination. There is no one size fits all model, unfortunately.
Mitigation Works
In some instances, the archaeological evaluation identifies archaeological remains of significance which require archaeological mitigation works which typically takes the form of excavation (sometimes referred to as strip, map and record), although a watching brief during construction works may sometimes be appropriate.
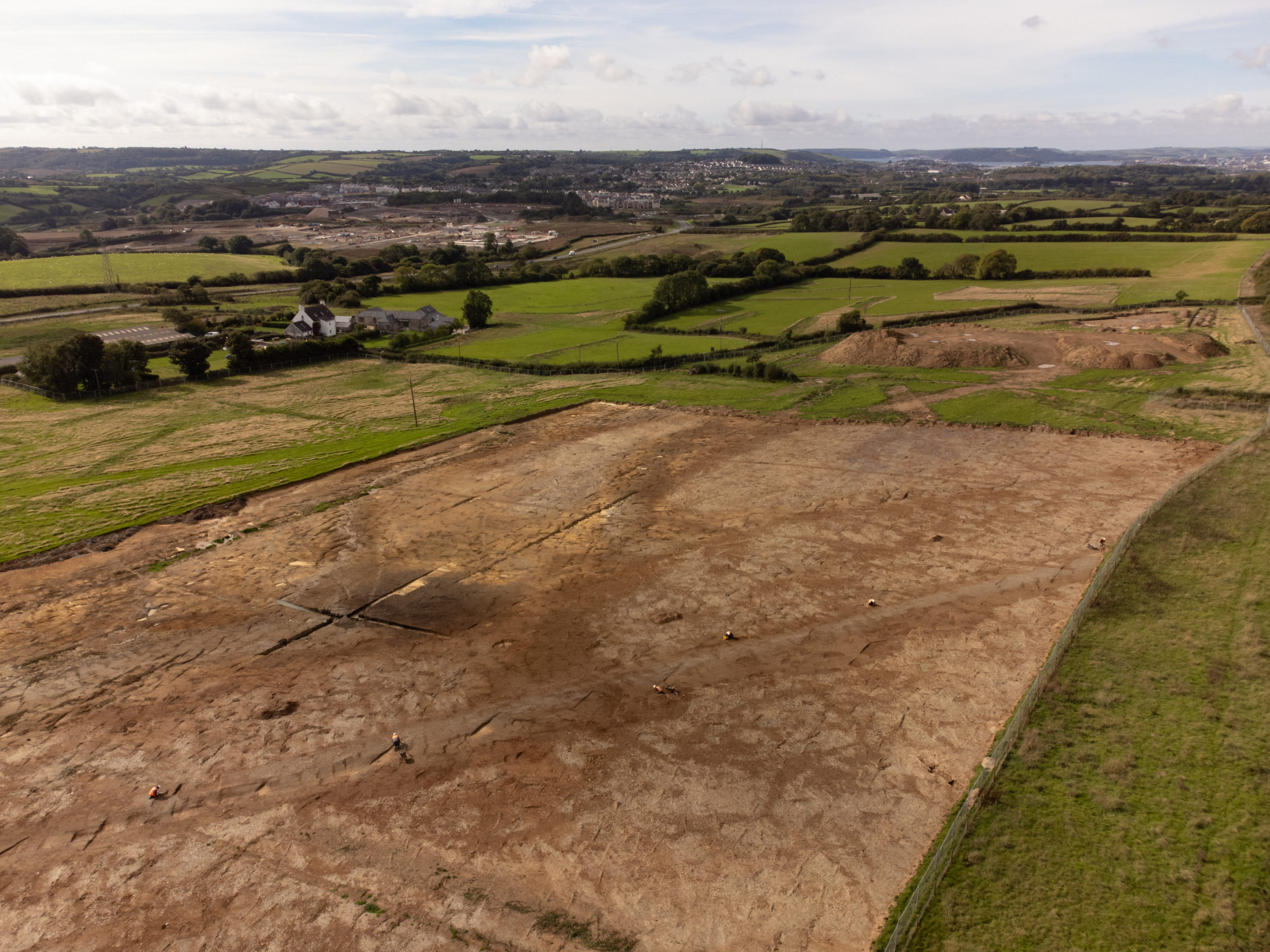

Once all fieldwork has been completed, construction works can generally commence whilst the archaeological post-excavation assessment, archiving and publication work is in progress. Occasionally archaeological remains are identified which are deemed worthy of preservation in situ which can require changes to the of development layout, which is why understanding the archaeological implications across sites at an early stage is key.
How can Orion assist?
Orion’s skilled archaeology team is experienced in advising landowners, developers and their agents on all aspects of potential and actual archaeological matters. Providing pragmatic support from the start of a project with land disposal or acquisition, right through to planning and the discharge of archaeological planning conditions.
As a CIfA Registered Organisation & accredited CIfA members, we problem solve with our clients in a timely and cost-effective manner. Our mix of specialist expertise and commercial understanding means we can be relied upon to deliver honest and accurate advice, negotiate favourable outcomes with statutory bodies, and establish and manage archaeological fieldwork.
Case Studies
The following case studies demonstrate Orion Heritage’s pragmatic & expert approach to sites where archaeological remains had the potential to become a challenge in advance of major residential development.
South Marston, Swindon
Clients: Hallam Land Management, Taylor Wimpey, Vistry & Hannick Homes
South Marston is a major, consented residential scheme for 2,380 homes, community facilities, a new primary school, and green space. Orion was appointed to undertake a heritage assessment and the heritage ES chapter for the outline planning application and then the discharge of the archaeological conditions on the outline consent.
Orion undertook a desk-based assessment, geophysical survey, and several phases of archaeological evaluations which identified multiple historic settlements and features, including Bronze Age, Iron Age and Roman. On our expert advice, the scheme layout was devised to exclude most of the large historic settlement to reduce both the potential impact on the remains and the cost of excavation. Our assessment also showed that there would be no effects on nearby listed buildings.
Orion formulated and agreed a site-wide outline archaeological mitigation strategy, which was written into the archaeological planning conditions. After planning permission was granted, we devised and agreed a thorough site-wide Written Scheme of Investigation and an outline archaeological management plan for the archaeological remains to be preserved in the open space of the scheme.
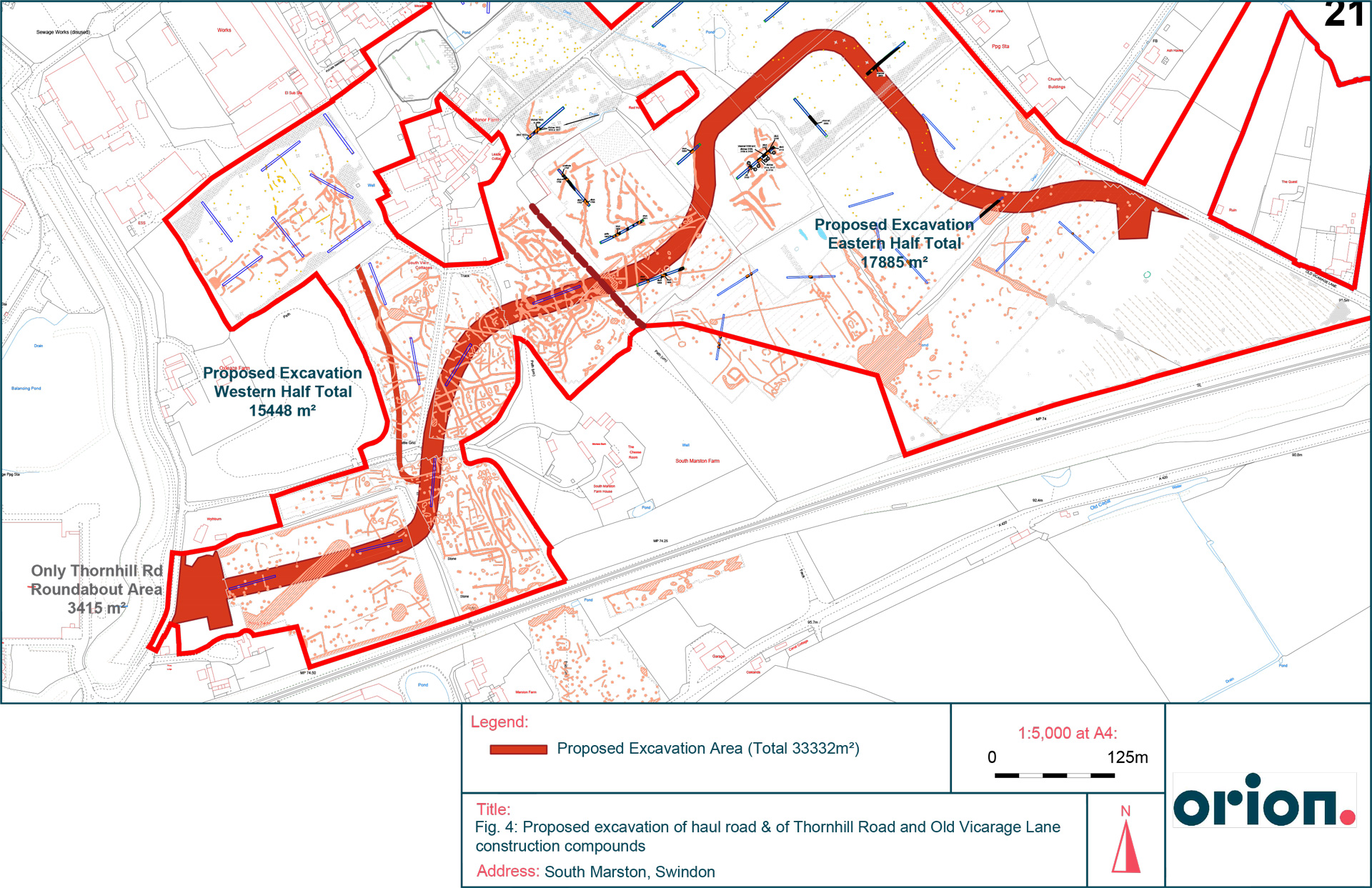
We continue to work with Taylor Wimpey & Vistry to run the large scale archaeological mitigation excavations required ahead of construction of this major residential scheme.
Land at Spa Road, Melksham
Clients: Hallam Land Management, Bloor Homes & Barratt David Wilson Homes
This is a consented scheme for 450 dwellings with land for medical or communal facilities and a relief road. Outline permission was granted in 2016 with a condition requiring mitigation investigations.
A member of Orion’s management team undertook an archaeological desk based assessment, organised & managed a geophysical survey of the site and managed pre-determination evaluation trenching while in previous employment. The geophysical survey revealed a focus of undated enclosures within part of the site. The evaluation trenching revealed that these enclosures were of Roman date with some slight evidence for a possible stone structure or stone surfaces. This was interpreted as being a small rural settlement typical of large parts of Wiltshire.
Following the granting of outline planning permission, Orion Heritage were appointed to agree the scope of mitigation excavation works on the area of Roman remains and manage the fieldwork and post-excavation works. The excavations revealed the remains of a Roman villa with a rudimentary underfloor heating system in parts of it. The building had been largely removed and only the traces of the foundations survived. An associated stone lined well was revealed which was approximately 2m in diameter and 5.5m deep dating to the 3rd & 4th centuries AD. Finds from the well included structural timbers, wooden stakes, a wicker basket, leather shoes, a large quantity of animal skulls and whole pots. The villa overlay a series of field systems within which were potential roundhouses which were the forerunners of occupation prior to the villa.
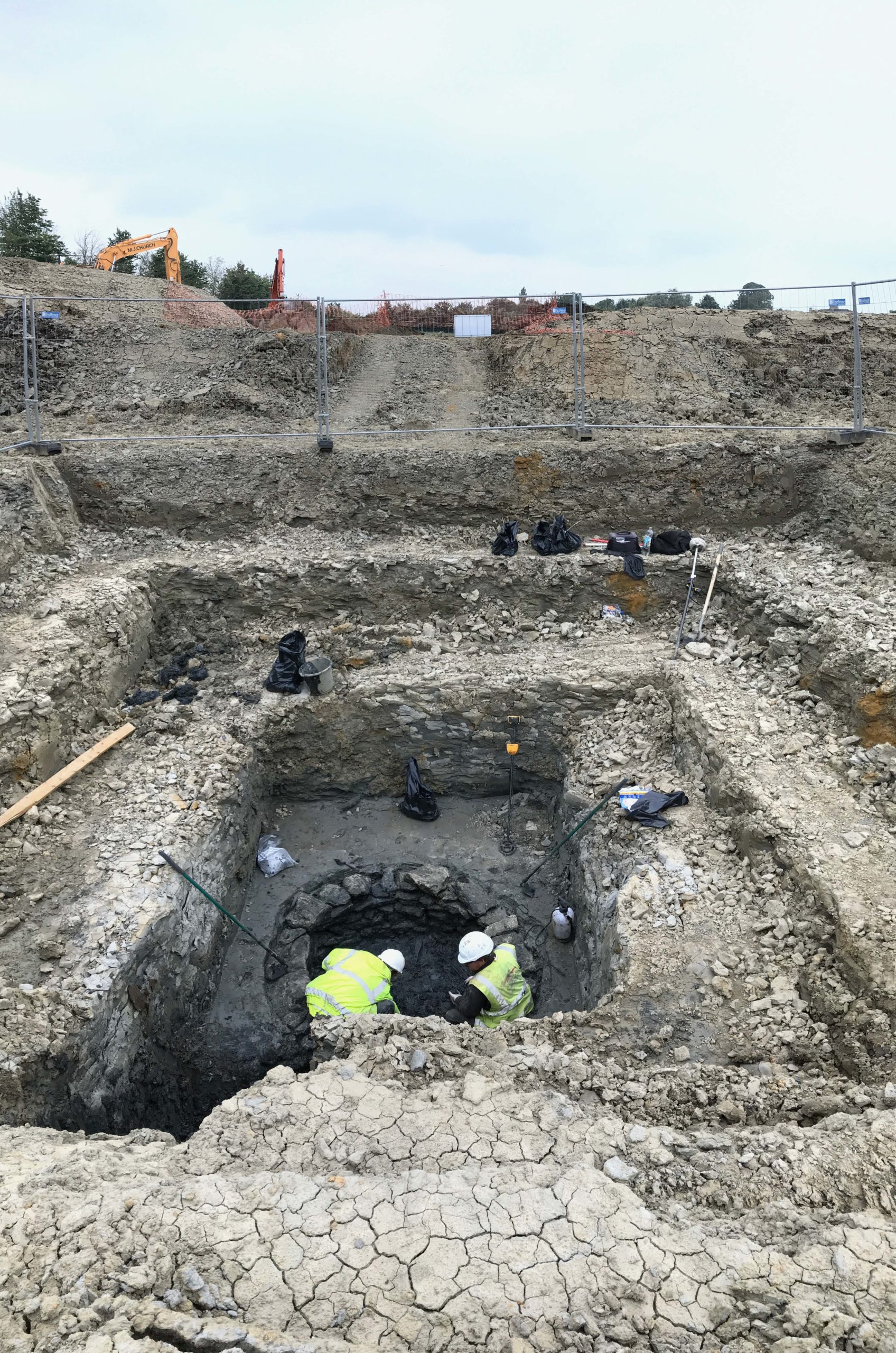

Despite the unexpected find of the villa and its well, the works were delivered on time well ahead of construction commencing. The well required a variation to the budget as this feature could not have been anticipated based on the results of the evaluation and geophysical survey.
Kingsbrook, Aylesbury
Client: Barratt David Wilson Homes North Thames
Kingsbrook is another major consented residential scheme for 2,450 homes, 10ha of employment uses, neighbourhood centre, 2 primary schools, eastern link road, green infrastructure, community facilities and flood defences. Following the granting of outline permission, Orion was appointed by BDW to progress the archaeological mitigation works required by the conditions of the outline consent.
Some pre-determination works had previously been undertaken comprising a geophysical survey of the whole site followed by some very limited and targeted trenching. In consultation with Buckinghamshire Council and the client, Orion agreed a site-wide mitigation strategy comprising evaluation trenching on a development phase by phase basis and mitigation excavation of 6 areas across the site. These investigations revealed late Iron Age/early Roman settlement and field systems as well as two associated cremation cemeteries and some limited Saxon activity. These works were completed within budget and within the timetable required, despite challenges posed by the Covid pandemic and wet ground conditions from inclement weather conditions.